Influence of ZrO2 nanoparticles on Tg and thermal stability of epoxy
Abstract
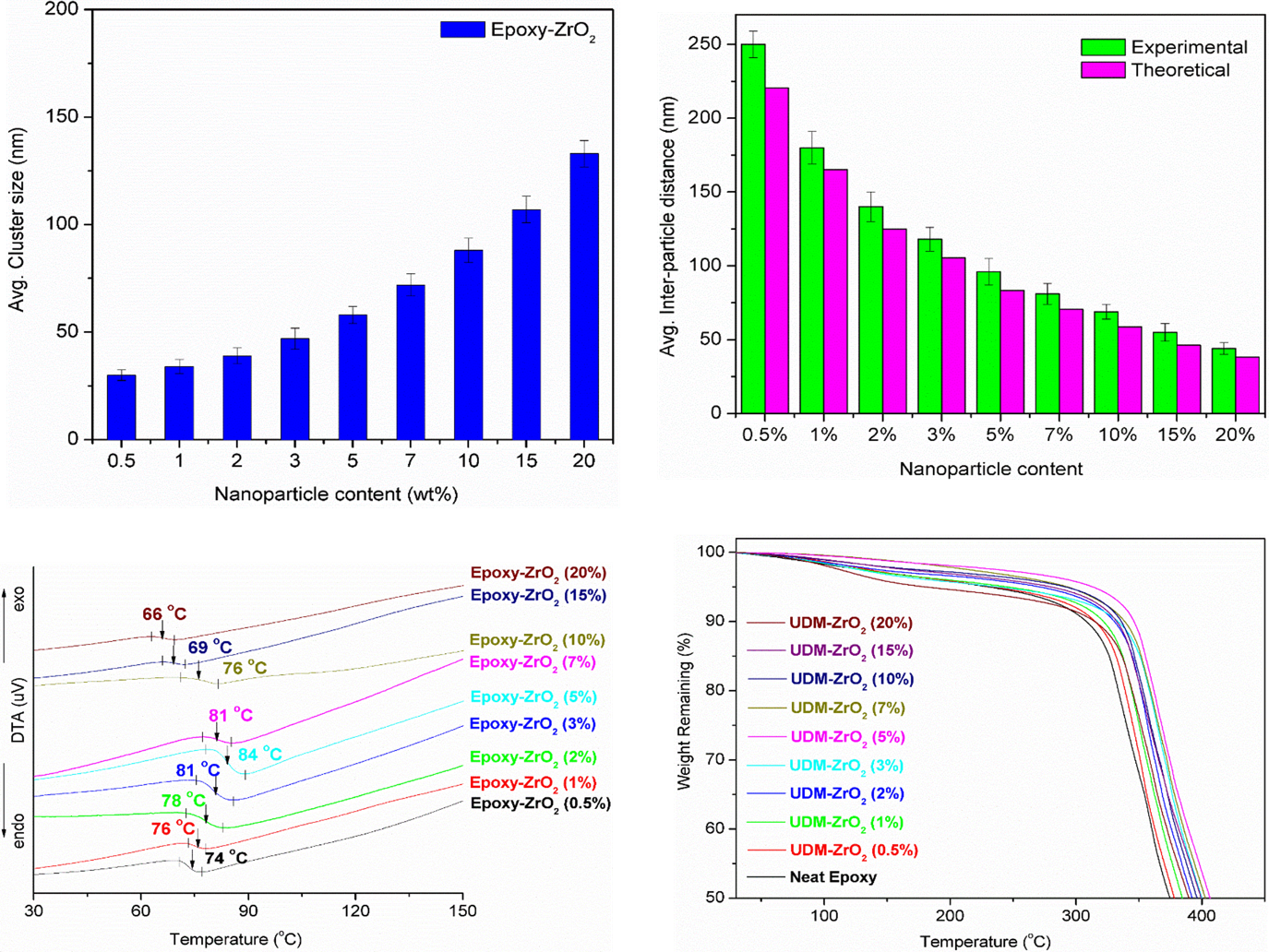
ZrO2 nanoparticles were loaded from 0.5 to 20 wt% into epoxy using an optimized ultrasonic dual-mixing procedure to investigate their influence on glass transition temperature (Tg), thermal stability. Tg and thermal stability of the nanocomposites were examined in relation to the size of nanoparticle clusters and interparticle spacing. Nanoparticle dispersion in epoxy was characterized using atomic force microscopy. Thermogravimetric analysis was utilized to investigate the thermal stability of the nanocomposites, while differential thermal analysis was employed to estimate Tg. It was discovered that a key threshold of approximately 5 wt% for significant increases in Tg and thermal stability is reached at this nanoparticle content. The reason for these improvements is that the uniform dispersion of the nanoparticles forces the establishment of a strong epoxy-nanoparticle interface, which limits the mobility of the epoxy polymer chains. Moreover, heat transfer through the matrix is restricted by the zirconia nanoparticles, which serve as thermal insulators.